- HEALTH
Unripe Momordica Charantia Ethanolic Extract Powder' to Combat Post-Meal Blood Sugar Spikes
Diabetes: The Silent Assassin Threatens Your Health!
with 6 million Koreans already diagnosed
Diabetes, often dubbed the "silent assassin", poses a serious threat to modern health. It’s a disease feared not only for its potential to cause severe complications but also for its ability to lead to death if left unchecked. According to the National Health Insurance Service, one in ten Koreans is diabetic, amounting to a staggering 6 million people nationwide. When considering those at the pre-diabetic stage, more than half of all adults in Korea need to manage their blood sugar levels. Alarmingly, three out of ten people with diabetes are unaware of their condition, making it even more dangerous. But what exactly is diabetes, this new red flag of health, and why does it occur?


Diabetes cannot be discussed without mentioning "blood sugar," which refers to the glucose (a type of carbohydrate) present in the blood. Maintaining a constant level of blood sugar is crucial for providing the body with a steady supply of energy. In a healthy body, blood glucose is transported throughout the system with the help of a hormone called insulin, allowing it to enter cells and be used for energy production. The balance of blood sugar is regulated by two key hormones produced by the pancreas: insulin and glucagon. Insulin helps lower blood sugar by facilitating the entry of glucose into cells, while glucagon raises blood sugar by releasing stored glucose into the bloodstream. The balance between these two hormones is vital for maintaining blood sugar homeostasis.

However, if the pancreas fails to produce sufficient insulin, or if the body's cells do not respond properly to insulin, diabetes symptoms emerge, leading to various harmful effects on the body.
Diabetes is a metabolic disease characterized by the body's inability to produce or properly use insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. This condition arises when glucose, instead of being absorbed by the cells for energy, remains in the bloodstream, resulting in high blood sugar levels. Over time, this can manifest in a range of symptoms and lead to the excretion of glucose in the urine. A particularly insidious aspect of diabetes is its tendency to progress without noticeable symptoms until the disease has significantly advanced. As a result, three out of ten people with diabetes are unaware of their condition, earning the disease its moniker as a "silent assassin." What makes diabetes especially dangerous is its potential to cause severe complications. These include diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, foot lesions, coronary artery disease, and cerebrovascular disease.

Diabetes can arise from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. A family history of diabetes increases the likelihood of developing the condition, while lifestyle factors like obesity, poor diet, lack of exercise, and aging contribute significantly to the growing number of diabetics. The symptoms of diabetes can be subtle or even unnoticeable when blood sugar levels are only slightly elevated, making it difficult to detect early on. However, as blood sugar rises, you might start to experience increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, vision problems, and excessive fatigue. If you notice these symptoms, it's important to consider the possibility of diabetes.
Even if you're not diagnosed with diabetes, your blood sugar might not be as safe as you think. If you've ever felt sudden fatigue, intense drowsiness, poor concentration, or extreme thirst after a meal, you might be experiencing a 'blood sugar spike.' These symptoms are often dismissed as mere food fatigue, but they are actually your body's warning signs that your blood sugar levels are rising too quickly.

A blood glucose spike is a rapid increase in blood sugar levels following a meal, typically marked by a rise of 50 mg/dL or more. When these spikes occur, the pancreas produces an excessive amount of insulin, which can eventually lead to insulin resistance. Insulin resistance reduces the effectiveness of insulin in managing blood sugar, causing levels to remain elevated. Over time, frequent blood sugar spikes can increase the risk of developing diabetes due to this insulin resistance.
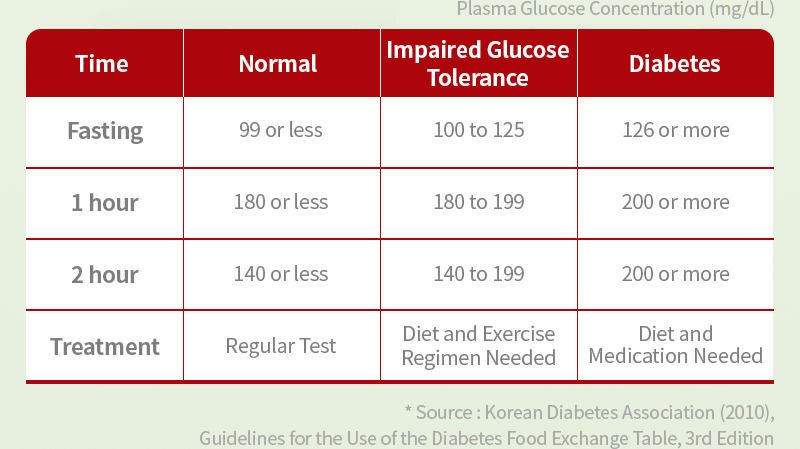
According to the World Health Organization, normal fasting blood glucose should be below 99 mg/dL, and blood glucose levels two hours after a meal should be less than 140 mg/dL. If your fasting blood glucose is between 100-125 mg/dL or your 2-hour postprandial blood glucose is between 140-199 mg/dL, you may have impaired glucose tolerance, a condition that can progress to diabetes. In such cases, it is crucial to control your diet and manage your weight to maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
Managing your blood sugar is fundamental to all of your health. To do this, glucose in the blood must be freely available for cellular utilization, and blood sugar spike after a meal must be prevented by suppressing the rapid rise in blood sugar. In this sense, health functional foods that can help suppress the rise in blood sugar after a meal can help maintain normal blood sugar by inhibiting carbohydrate-degrading enzymes in the intestine or improving insulin resistance. One ingredient is particularly beneficial for blood sugar management, which is called 'Unripe Momordica Charantia Ethanolic Extract Powder.

Unripe Momordica Charantia' is a loofah-like gourd plant that grows in the tropics, which is harvested in Korea mainly during the summer season. Its green fruit turns into from yellow-orange to almost red and bitter as it ripens. The 'Unripe Momordica Charantia,' which has no seeds, contains 'gaba' (Y-aminobutyric acid), which is individually approved by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety as a functional ingredient that can 'help suppress postprandial blood sugar rise' and is good for blood sugar management. In particular, it is recommended to use unripe seeds within 20 to 25 days after flowering, not mature seeds, which produce toxins in the seeds when they mature.
'Banaba Leaf Extract' is also beneficial, which is derived from banana leaf, a medicinal crop that has long been used in Southeast Asia, including the Philippines, Indonesia, and Japan. This is because the extract contains a compound called corosolic acid, which helps to control blood sugar spikes.
| Functional Ingredient Name | Unripe Momordica Charantia Ethanolic Extract Powder | Banaba Leaf Extract |
|---|---|---|
| Daily Recommended Intake | 2.4 g/day | 0.4 to 1.3 mg/day of corosolic acid, an indicator compound |
| Function | May help control postprandial blood sugar spikes | May help control postprandial blood sugar spikes |
| Mechanism of action | Suppresses glucagon and reduces de novo gluconeogenesis | Active GLU4 and promote glucose consumption |
Even if diabetes doesn’t run in your family, westernized eating habits and lack of exercise can still put you at risk. Food plays a crucial role in maintaining normal blood sugar levels after meals. Fast-absorbing simple sugars—found in sugar, honey, soft drinks, and certain fruits—can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar, which are harmful. Instead, opt for whole grains, brown rice, and vegetables rich in fiber, as they slow down the absorption of sugars. Additionally, incorporating health functional foods that help regulate blood sugar into your routine is a smart preventive measure—after all, you never know when or where the silent assassin, diabetes, might strike.





